객체 지향 3대 요소 / 다형성
26 Aug 2021 -
2 minute read
-
객체 지향 3대 요소
-
캡슐화(Encapsulation) = 정보 은닉(data hiding)
-
상속(Inheritance) = 재사용 + 확장
-
다형성(Polymorphism) = 사용편의
-
-
다형성
-
하나의 객체가 여러 가지 형태를 가질 수 있는 것
-
유연하고 확장성 있으며, 유지보수가 편리한 프로그램을 만들 수 있음
-
- 객체 타입에서의 다형성 : 여러 역할을 가짐
- 메서드의 다형성 : 같은 타입을 구현하는 객체타입 but 각각 다르게 동작
-
-
예제) GOLD 등급 만들기 : 제품 구매 시 10% 할인 / 포인트 2% 적립
-
Customer.java
public class Customer { protected String customerName; protected String customerGrade; int bonusPoint; double bonusRatio; //포인트 적립률 public String getCustomerName() { return customerName; } public Customer(String customerName, int bonusPoint) { this.customerName = customerName; this.bonusPoint = bonusPoint; customerGrade = "SILVER"; bonusRatio = 0.01; } public int calcPrice(int price) { bonusPoint += (int)(price * bonusRatio); //구매 가격의 *0.01 만큼 포인트 적립 return price; } public String showCustomerInfo() { return customerName + "님의 등급은 " + customerGrade + "이며, 보너스 포인트는 " + bonusPoint + " 점입니다."; } } -
VIPCustomer.java
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{ double salesRatio; //할인률 public VIPCustomer(String customerName, int bonusPoint) { super(customerName, bonusPoint); customerGrade = "VIP"; bonusRatio = 0.05; salesRatio = 0.1; } @Override public int calcPrice(int price) { bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio; price -= (int)(price * salesRatio); return price; } public String showCustomerInfo() { return customerName + "님의 등급은 " + customerGrade + "이며, 보너스 포인트는 " + bonusPoint + " 점입니다."; } } -
GoldCustomer.java
public class GoldCustomer extends Customer { double salesRatio; public GoldCustomer(String customerName, int bonusPoint) { super(customerName, bonusPoint); customerGrade = "Gold"; salesRatio = 0.1; bonusRatio = 0.02; } public int calcPrice(int price) { bonusPoint += price + bonusRatio; return price - (int)(price * salesRatio); } } -
Main.java
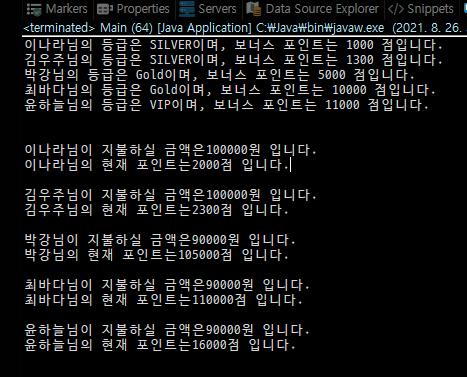
import java.util.ArrayList; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Customer> customers = new ArrayList<>(); Customer customerA = new Customer("이나라", 1000); Customer customerB = new Customer("김우주", 1300); Customer customerC = new GoldCustomer("박강", 5000); Customer customerD = new GoldCustomer("최바다", 10000); Customer customerE = new VIPCustomer("윤하늘", 11000); customers.add(customerA); customers.add(customerB); customers.add(customerC); customers.add(customerD); customers.add(customerE); for (Customer customer : customers) { System.out.println(customer.showCustomerInfo()); } System.out.println(); int price = 100000; for (Customer customer : customers) { int cost = customer.calcPrice(price); System.out.println("\n" + customer.getCustomerName() + "님이 지불하실 금액은" + cost + "원 입니다."); System.out.println(customer.getCustomerName() + "님의 현재 포인트는" + customer.bonusPoint + "점 입니다."); } } } -
출력결과
-